China tariffs have become a focal point in recent discussions surrounding U.S. trade relations, as tensions between the two countries continue to escalate. With President Trump signaling his intent to impose steep tariffs on Chinese imports, the potential implications for the China economy are alarming. Economists warn that these tariffs could backfire, leading to higher prices for American consumers, disrupted supply chains, and weakened connections with international allies. As U.S. imports from China decline, the broader impact on global markets and the U.S. economy cannot be overlooked. Understanding the dynamics surrounding China tariffs is essential for grasping the future of both domestic and international commerce.
In the ongoing discourse about trade disputes, the implementation of duties on goods from China is under scrutiny, particularly regarding its potential fallout. The prospect of imposing hefty levies, often referred to as tariffs, raises questions about the effects on bilateral commerce and economic stability. Analysts highlight concerns that the escalation of such trade barriers could hinder economic growth in both nations, while also complicating logistics and supplier networks across borders. These trade measures have broader implications that extend beyond mere statistics, affecting everything from consumer prices to diplomatic relationships. Delving into the nuances of these trade taxes is crucial for understanding their far-reaching consequences on global economic landscapes.
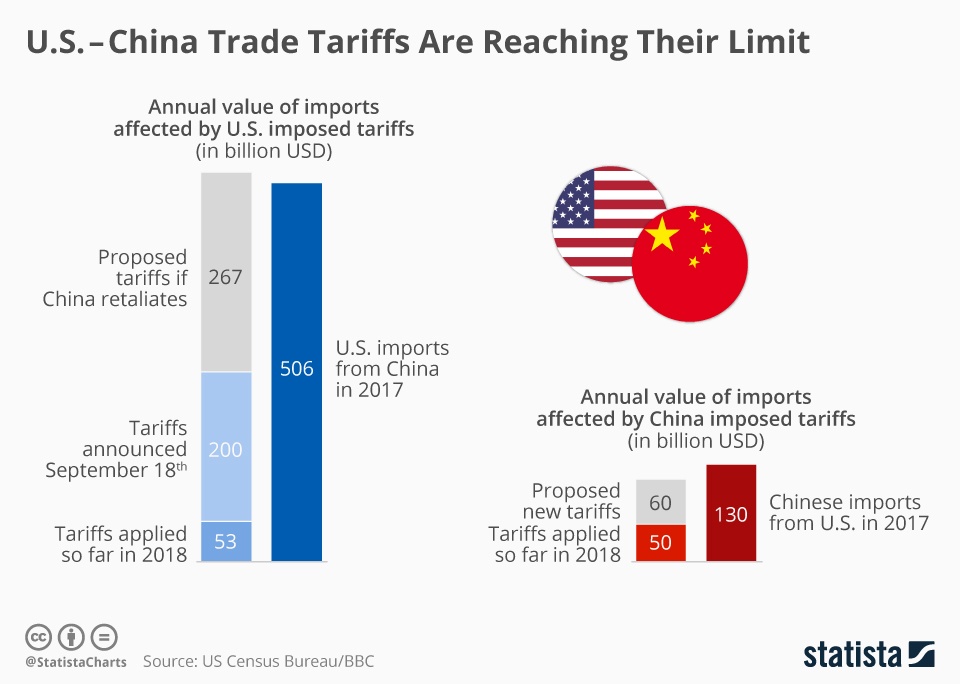
The Economic Consequences of China Tariffs
The implementation of China tariffs could have a substantial impact on both the U.S. and Chinese economies. Economists warn that aggressive tariffs imposed on imports from China may lead to an increase in prices for American consumers. This is not just a theoretical concern; historical data have shown that tariffs can lead to higher costs of goods as manufacturers often pass the increased costs onto consumers. With products like smartphones and laptops heavily reliant on components made in China, a surge in tariffs means Americans could see significant increases in everyday costs.
Moreover, the repercussions of China tariffs extend beyond inflated prices. Such tariffs could disrupt existing supply chains that have been established over decades, which could affect not only American companies but also those in China. Industries dependent on raw materials and intermediate goods from China could face delays and shortages, leading to stalled production and potential job losses. The resulting economic instability could strain U.S. trade relations further and challenge the ability of American manufacturers to compete in a global market.
U.S.-China Trade Relations Under Pressure
Recent discussions about a potential resurgence of tariffs underscore the tense state of U.S.-China trade relations. Government officials have signaled a willingness to escalate trade tensions, which could lead to a new round of tariffs reminiscent of those imposed during the Trump administration. These tariffs not only strain diplomatic ties but also bring to the forefront the complexities of a globalized economy where interdependence has grown over the years. With China being a major supplier of goods, any punitive measures could drastically alter the dynamics of international trade.
The implications of heightened tariffs also touch on broader foreign relations. As the U.S. imposes tariffs, it risks pushing China closer to its traditional allies in Europe and the Asia-Pacific region. This shift could lead to the formation of new economic alliances, potentially sidelining U.S. interests on the global stage. Tariffs could become a catalyst for China to solidify relationships with other nations, fostering a strategic bloc that could challenge U.S. dominance in international trade.
Impact on the China Economy
China’s economy, already facing challenges like stagnating consumer demand and a struggling housing market, could be severely impacted by new tariffs. A systematic approach to imposing tariffs as high as 60% may effectively cripple China’s export sector, which has long relied on the U.S. market. Although China is pursuing alternative markets, such as those in Southeast Asia and Africa, the immediate repercussions of tariffs could be devastating, driving down economic growth rates that are vital for maintaining social stability.
Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding tariff implications could hamper China’s response strategy. Businesses in China are likely to experience volatility, as the inability to predict the nature and extent of tariffs could lead to cautious investment decisions. Economists warn that this unpredictability could also trigger domestic unrest, as citizens become increasingly concerned about rising prices and stagnating wages, adding additional pressure on the Chinese government to respond effectively to U.S. trade policies.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Effects
The potential for supply chain disruptions due to new tariffs on Chinese goods cannot be overstated. Many American companies depend on a complex web of supply chains that include parts and materials sourced from China. Implementing higher tariffs inevitably affects these companies’ cost structures, which may prompt them to reconsider their sourcing strategies or pass the costs onto consumers. This change in dynamics could lead to substantial delays in production and the rollout of goods in various sectors, from technology to automotive.
As companies scramble to mitigate these disruptions, they may seek alternate suppliers outside of China, which poses its own challenges. Countries like Vietnam and India have been highlighted as potential beneficiaries of U.S. companies looking to shift their supply chains. However, the immediate infrastructure and logistical capabilities of these countries may not match those of China, resulting in a lag before any real transition can occur. Ultimately, these disruptions could lead to broader challenges across many industries, affecting job markets and economic stability in the U.S.
The Role of U.S. Imports from China
U.S. imports from China play a pivotal role in a vast array of sectors, making any potential trade disruptions particularly concerning. Data shows that products ranging from consumer electronics to everyday household goods are sourced in large part from China. If tariffs were to drastically increase, the immediate consequence would likely be a spike in product prices, directly impacting American consumers. This necessitates immediate action and consideration from American businesses and policymakers alike.
In addition, the ramifications of decreased imports from China could echo throughout the economy. Manufacturers may encounter problems with fulfilling demand, leading to potential revenue losses. Long-term, if companies are unable to secure competitive pricing from alternative suppliers, the implications could lead to reduced selection for consumers and slower economic growth. Hence, understanding the dynamics of U.S. imports from China is crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade.
Trump Tariffs: A New Era of Trade Warfare?
The anticipated return of Trump’s tariff policies signals a coming period of intense trade scrutiny and potential conflict. While designed to protect U.S. interests, tariffs could provoke retaliatory measures from China, leading to a full-blown trade war. Economists argue that hitting China with excessive tariffs could hinder the American economy by disrupting trade flows and triggering inflationary pressures. Furthermore, such actions may alienate traditional U.S. allies and push China to forge new partnerships that could nullify any advantages sought by tariffs.
These tariffs could lead to unintended consequences that reshape the global economic landscape. If tariffs result in increased costs for American businesses and consumers, U.S. trade relations could deteriorate further, prompting other countries to re-evaluate their alliances. This could provide China with an opening to strengthen ties with other economic powers, potentially changing the balance of power in international trade.
Labor Shortages and Economic Implications
Labor shortages are another critical dimension to consider when discussing the implications of China tariffs. As companies anticipate potential disruptions and rising costs due to tariffs, they may begin to scale back their operations, leading to layoffs or hiring freezes. This not only impacts the immediate workforce but can also discourage young talent from entering industries heavily reliant on trade with China. The risk is a declining pool of skilled labor, making it difficult for businesses to rebound quickly from any economic downturn caused by tariffs.
Moreover, as American firms struggle to adapt to new tariffs and rising costs, there could be a shift in strategies that focus more on automation and efficiency rather than workforce expansion. This move could lead to increased unemployment rates among certain demographics, exacerbating social tensions and contributing to a rise in economic inequality. The long-term effects of labor shortages could significantly reshape the U.S. economy, making it essential to closely monitor and analyze these trends.
China’s Strategic Adaptations Amid Tariffs
In anticipation of renewed tariffs, China has been strategizing on how to mitigate the potential fallout. Enhancing relationships with other regional powers and pursuing initiatives aimed at increasing exports to emerging markets are part of China’s broader economic strategy. This could involve diversifying the countries they trade with to offset losses that may result from U.S. tariffs, thereby stabilizing their economy amid uncertainty. Initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative exemplify this aim of broadening economic ties.
Furthermore, China may also look inward by amplifying domestic consumer spending initiatives, promoting products developed in China abroad while simultaneously minimizing dependency on U.S. markets. Such strategies may not fully eliminate the economic strain caused by U.S. tariffs, but they could alleviate some of the pressures faced by the Chinese economy in this critical time. Understanding how China adapts will be crucial for U.S. policymakers as they navigate the complexities of international trade relations.
Building Alliances in Response to U.S. Trade Policies
Faced with the prospect of increased tariffs and economic isolation, China’s government is likely to intensify efforts to forge alliances with other nations. By positioning itself as a victim of U.S. trade aggression, China can rally support from other countries that view the U.S.’s approach to tariffs as a threat to global trade norms. Countries such as the EU, Japan, and Australia could be strategic partners in this regard, as they may also face trade barriers under a renewed U.S. tariff regime.
Bilateral and multilateral agreements could be on the horizon, as China seeks to enhance its global influence through cooperative economic partnerships. This diplomatic maneuvering could lead to a reshaping of global trade alliances, where nations band together to counteract perceived U.S. hostility. Such collaborations may not only serve to assist the Chinese economy but could also redefine the landscape of international trade relationships in a way that diminishes U.S. economic power.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do China tariffs impact U.S. trade relations?
China tariffs significantly affect U.S. trade relations by increasing costs for American businesses that rely on Chinese imports. This can lead to higher consumer prices, strained economic ties, and potential retaliation from China, complicating negotiations and trade agreements.
What are the potential economic impacts of Trump’s tariffs on China’s economy?
Trump’s tariffs could severely impact China’s economy by disrupting exports essential for economic growth. A higher tariff rate of 60% may lead to dwindling sales in the U.S. market, further aggravating China’s economic challenges and encouraging them to seek new markets in Asia and beyond.
Could supply chain disruptions occur due to increased tariffs on U.S. imports from China?
Yes, increased tariffs on U.S. imports from China could lead to supply chain disruptions. Companies that depend on Chinese manufacturing may face delays and increased costs, forcing them to find alternative suppliers, which can be challenging and time-consuming.
How do China tariffs affect consumer prices in the U.S.?
China tariffs are likely to drive up consumer prices in the U.S. as businesses pass on the increased costs for imported goods. This can lead to inflationary pressures, affecting the purchasing power of American consumers and potentially slowing down economic growth.
What strategies is China using to counter the effects of U.S. tariffs?
To counter the effects of U.S. tariffs, China is diversifying its export markets, investing in the Belt and Road Initiative, and fostering trade relations with other developing countries to reduce dependency on U.S. imports and maintain its economic stability.
What could be the long-term effects of tariffs on U.S.-China relations?
The long-term effects of tariffs on U.S.-China relations could include a sustained trade war, weakened cooperation between the two nations, and a shift in global alliances, as countries may seek closer ties with either the U.S. or China in response to ongoing tariff disputes.
How might China retaliate against U.S. tariffs?
China might retaliate against U.S. tariffs by imposing its own tariffs on American goods, affecting exports from the U.S. to China. This could escalate tensions and lead to a broader trade conflict, further impacting international markets and economies.
Which countries could benefit from reduced U.S. imports from China?
Countries like Vietnam, India, and Mexico are likely to benefit from reduced U.S. imports from China as they may step in to fill gaps in the supply chain. However, adapting to meet U.S. quality and production standards can take time.
What role do tariffs play in U.S. trade policy towards China?
Tariffs are central to U.S. trade policy towards China, serving as leverage to negotiate better trade terms. They aim to reduce the trade deficit and protect American industries, but can also create unintended consequences such as escalating prices and strained diplomatic relations.
How do tariffs impact the global economy?
Tariffs can disrupt the global economy by altering trade patterns, increasing costs for consumers, and fostering uncertainty among businesses. This may lead to decreased international investment and slower economic growth globally, as trade wars can affect multiple countries.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact on China’s Economy | Potential tariffs could harm China’s export-driven economy, exacerbating existing domestic issues such as a struggling housing market and low consumer demand. |
| U.S. Economic Consequences | Higher tariffs may lead to higher prices for American consumers, disrupt supply chains, and result in labor shortages. |
| U.S. Foreign Relations | Increased tariffs could drive China closer to U.S. allies in Europe and Asia, undermining traditional U.S. alliances. |
| Negotiation Potential | China may see new tariffs as an opportunity to negotiate better trade terms, possibly aiming for a revised trade agreement similar to the previous Phase One deal. |
| Preparations in China | China has been strategizing for potential tariffs since it became likely Trump could be re-elected, focusing on protecting domestic markets and stimulating economic growth. |
Summary
China tariffs are poised to create both economic and geopolitical repercussions, impacting not only the U.S. economy but also its foreign relations. Trump’s promise to impose substantial tariffs introduces uncertainty, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers and supply chain disruptions. As China grapples with its own economic challenges, these tariffs could inadvertently strengthen ties between Beijing and traditional U.S. allies, posing long-term risks to America’s global relationships.