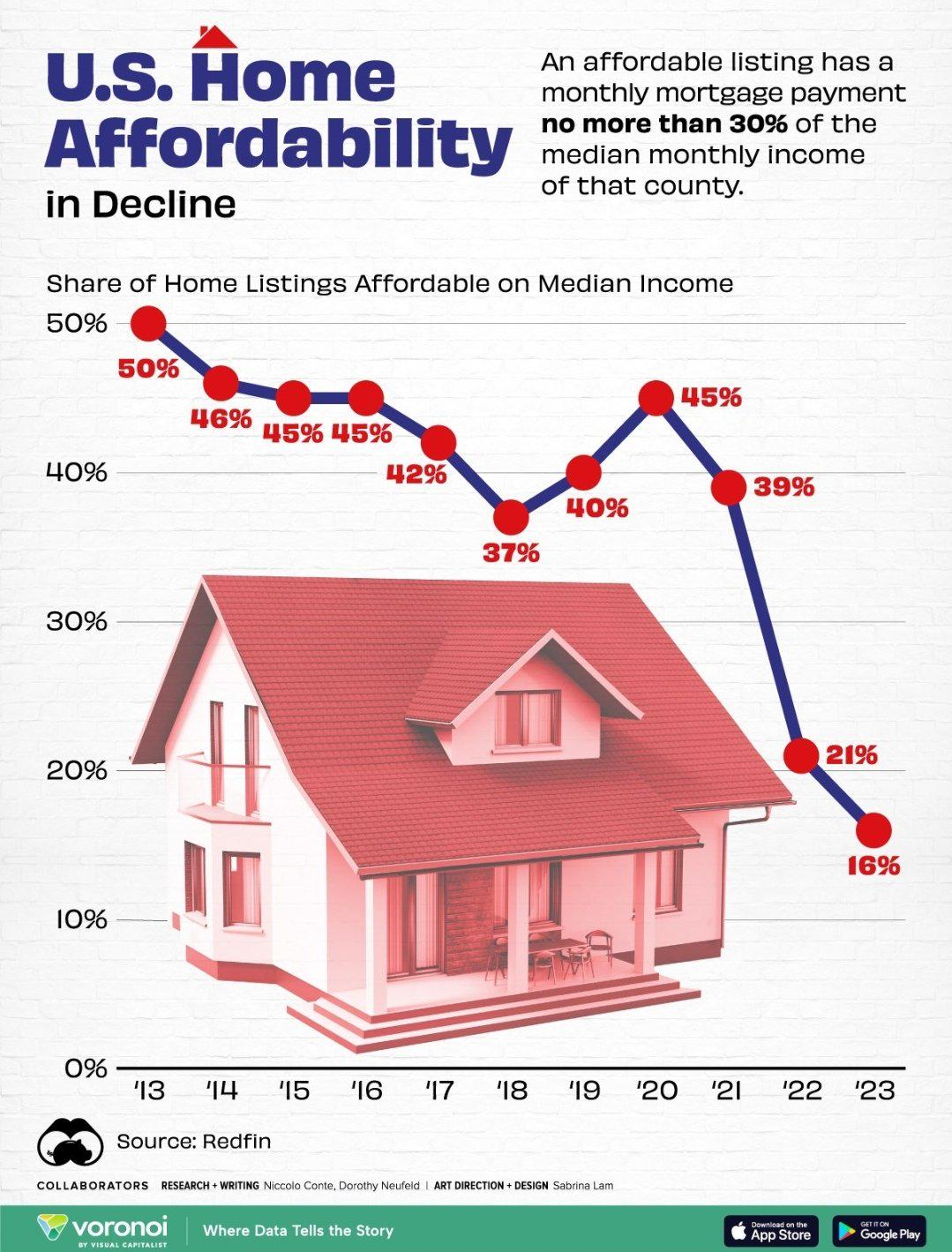
The United States is grappling with a persistent housing affordability crisis that is pushing homeownership further out of reach for an increasing number of Americans. With the cost of new single-family homes more than doubling since 1960, it’s clear that the current housing market trends are unsustainable. Contributing to this crisis are strict land-use regulations that inhibit construction productivity, effectively stifling the ability of builders to create more affordable housing options. NIMBY policies, which resist new developments in local neighborhoods, exacerbate homeownership challenges by limiting supply in high-demand areas. As the gap between available housing and demand widens, the affordability of homes continues to be a pressing issue that requires urgent attention from policymakers and stakeholders.
As we delve into the ongoing crisis surrounding housing costs, it’s important to acknowledge the myriad challenges facing prospective homeowners. This situation, often referred to as the housing affordability dilemma, is characterized by rapidly escalating prices that starkly contrast with the stagnant wages for many families. The impact of restrictive land-use policies and local opposition to new property developments have created a difficult landscape for builders, while simultaneously hobbling efforts to innovate in construction. Additionally, these hindrances have increased the gap in wealth and opportunity across generations, making the prospect of homeownership more elusive than ever. By exploring the interconnectedness of these factors, we can better understand the underlying dynamics at play in this critical economic issue.
The Housing Affordability Crisis Explained
The housing affordability crisis has emerged as a significant concern across the United States, where rising home prices and stagnant wages have created a rift between income levels and homeownership potential. Various factors contribute to this growing predicament, including tight land-use regulations that exacerbate the problem by limiting the scale of new housing developments. In many regions, especially those grappling with NIMBY policies, the ability to build new structures is incredibly hindered, exacerbating supply shortages and driving prices even higher. Consequently, these challenges make homeownership appear increasingly unrealistic for many within the middle class.
Moreover, the crisis is also characterized by the significant disparity between urban and suburban housing costs. While large metropolitan areas face soaring prices that leave many potential homeowners priced out, surrounding areas often struggle with their economic development due to a lack of sufficient infrastructure and housing options. These disparities are further heightened by ongoing economic shifts and the rise of remote work, leading to evolving housing market trends that continuously reshape buyer expectations. The complexity of these issues reveals that addressing the affordability crisis requires a nuanced understanding of both economic pressures and local policies.
Impact of NIMBY Policies on Construction Productivity
NIMBY—or “Not In My Backyard”—policies play a pivotal role in influencing construction productivity, as they often lead to stringent regulations that limit the size and scope of new housing projects. These local policies arise from community concern about various aspects, such as increased traffic, changes in neighborhood character, or potential decreases in property values. Unfortunately, while these regulations aim to maintain community standards, they significantly impede the ability of builders to create homes en masse, effectively stifling innovation and cost-effective construction practices. As a result, the housing market is flooded with bespoke builds instead of more affordable, mass-produced options.
This bottleneck not only impacts the rate of new home development but also amplifies construction costs. With smaller projects becoming the norm, builders find themselves less inclined to invest in the innovative technologies that could enhance productivity and drive down expenditures. Historical comparisons reveal that pre-1970, the construction sector thrived alongside booming industries like automotive manufacturing. In contrast, present-day construction suffers from diminished productivity, with firms being unable to exploit economies of scale that previously defined housing development. Thus, the intertwining of NIMBY policies and reduced construction productivity poses a dual threat to the already precarious state of housing affordability.
Analyzing Housing Market Trends and Future Solutions
The trends observed in the housing market provide critical insights into the factors shaping current conditions. As homeownership challenges continue to rise, particularly for younger demographics, understanding the systemic issues at play becomes increasingly important. Data show a stark decline in housing starts and new constructions, indicating that external regulatory pressures and community-driven opposition are making it harder to meet the demands of the housing market. The dip in construction productivity highlights not only an industry in crisis but also the dire need for concerted policy action that facilitates housing development without sacrificing community integrity.
Addressing these trends requires innovative solutions that reconcile the need for affordable housing with community interests. One potential avenue lies in reforming land-use regulations that currently impede large-scale construction projects. By reevaluating zoning laws and shifting away from restrictive policies, local governments can create environments more conducive to new developments. Encouraging collaborative discussions between builders, local officials, and community members about the type of developments desired can also foster greater understanding and pave the way for building homes that meet both community standards and affordability needs.
Land-Use Regulations and Their Economic Consequences
Land-use regulations, while often perceived as protective measures for communities, have profound implications on the broader economy, particularly in the housing sector. The growing complexity of these regulations has resulted in a decline in construction productivity—this phenomenon underscores how governmental and local policies can create unintended economic consequences. The more these regulations dictate project specifics, the fewer companies there are willing to take on large-scale developments. This trend has led to a fragmented industry where smaller builders dominate the market, often at the expense of innovation and efficiency.
Furthermore, this misalignment between regulatory frameworks and economic realities illustrates a systemic issue where policies intended to safeguard local environments inadvertently preserve a status quo that hampers economic growth. The implications are significant; as construction slows due to cumbersome regulations, rising housing inventory becomes stagnant, further fueling the affordability crisis. Thus, a reevaluation of land-use policies is essential to stimulate construction productivity and promote a more flexible and proactive housing market.
Homeownership Challenges for Today’s Generation
Today’s younger generations face unprecedented challenges in achieving homeownership, a crucial milestone often associated with stability and economic success. With soaring prices and stricter mortgage requirements, many find themselves trapped in a cycle of renting without the prospect of financial advancement through home equity. This challenge is compounded by stagnant wages, an increase in student debt, and, importantly, soaring housing costs driven by restrictive land-use policies and NIMBY sentiments that limit housing supply.
The ramifications of these challenges extend beyond individual circumstances, affecting the broader economy and community development. With fewer young people able to buy homes, neighborhoods risk declining in both economic vibrancy and demographic diversity. Homeownership has profound intergenerational effects, creating wealth accumulations that can be passed down, thus affecting familial economic stability. Recognizing these challenges opens the door for discussions surrounding policy reforms that prioritize housing accessibility and solutions to bolster the homeownership prospects of the younger generation.
Promoting Construction Productivity: Innovative Approaches
Boosting construction productivity stands as a critical element in resolving the housing affordability crisis. Innovative approaches can include the adoption of modular building techniques and advanced construction technologies, which facilitate quicker construction times and lower costs. Emphasizing efficiency and standardization in the building process aligns closely with the historical precedents that underscored America’s post-war housing boom, where large-scale developments thrived due to their efficient productivity models.
Incorporating modern technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and automated construction processes can help counteract the stagnation seen in the construction industry since the 1970s. By leveraging advancements that streamline project management and construction workflows, builders can combat the limitations imposed by land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. A shift toward innovative solutions could lead to a rejuvenation in construction activity, ultimately pushing boundaries on both affordability and availability in the housing market.
The Role of Economic Policy in Housing Solutions
Economic policy plays a strategic role in tackling the multifaceted issues inherent in the housing sector. By implementing policies that incentivize construction amidst the constraints of land-use regulations, governments can stimulate housing production, making homeownership more attainable for individuals and families. Focused policy reforms aimed at easing restrictions on development, particularly in high-demand regions, can create a more favorable environment for builders while also addressing community concerns.
Furthermore, economic policy should prioritize equitable housing strategies aimed at mitigating the generational wealth gap exacerbated by the housing crisis. Initiatives that support first-time homebuyers, such as grants or tax credits, can empower aspiring homeowners and promote more inclusive ownership patterns. By aligning economic policy with innovative housing solutions, an integrated approach can uplift communities and rejuvenate the housing market while ensuring that all citizens have the opportunity to realize their dream of homeownership.
Community Engagement and Housing Development
Effective community engagement is crucial in bridging the gap between developers and residents when it comes to housing projects. When developers actively involve community members in the planning process, it mitigates NIMBY sentiments, paving the way for smarter, more inclusive development strategies. By fostering open dialogues that allow residents to voice their concerns and desires, builders can create housing solutions that are more likely to gain local support, ensuring that new projects reflect community needs and expectations.
Moreover, engaging the community can contribute to smoother regulatory processes, as informed residents may be more amenable to changes that incorporate their feedback. This collaborative approach can lead to innovative designs and increased acceptance of high-density developments that combat the housing affordability crisis. Ultimately, community engagement not only enhances the credibility of developers but also establishes a foundation for trust and cooperation, critical elements in creating sustainable neighborhoods.
Future Trends in Housing: Innovation and Adaptability
Looking ahead, the landscape of housing is bound for significant transformation driven by innovation and adaptability. With increasing emphasis on sustainable building practices and smart home technologies, the future of housing presents unique opportunities to address current challenges head-on. Adapting to changing market demands will require the construction sector to pivot towards energy-efficient designs and versatile living spaces that cater to diverse populations.
Furthermore, trends such as remote work and population shifts towards urban centers require new housing models that respond to evolving lifestyle preferences. Home builders must remain agile in their approach, embracing technological advancements that enhance construction productivity and affordability. As the demand for homes continues to rise, the integration of innovative solutions will play a pivotal role in shaping resilient housing markets capable of meeting the diverse needs of forthcoming generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is contributing to the housing affordability crisis in the U.S.?
The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. is largely driven by a combination of factors, including rising construction costs and stringent land-use regulations. These regulations often incorporate NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies that hinder large-scale housing developments, thereby reducing the overall supply of affordable homes in the market.
How do land-use regulations impact housing affordability?
Land-use regulations can significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by restricting the size and type of construction projects. This leads to smaller builders who often lack the resources and scale necessary to implement cost-saving innovations, ultimately driving up home prices and limiting the availability of affordable housing options.
What role do NIMBY policies play in the housing market trends?
NIMBY policies often result in prolonged approval processes for housing projects, which can slow down construction and deter developers from investing in new builds. This contributes to a stagnation in the housing supply, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis as demand continues to outpace available homes.
Why is construction productivity declining in relation to the housing market?
Construction productivity has been on the decline since the 1970s, in part due to increased land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. These regulations limit the scale of building projects, reducing economies of scale and preventing the mass production of homes, which can lower costs and improve affordability for buyers.
What challenges are faced by potential homeowners in today’s housing market?
Potential homeowners face significant challenges in today’s housing market due to the ongoing housing affordability crisis. High prices, driven by limited supply caused by restrictive land-use regulations and lower construction productivity, make it increasingly difficult for individuals and families to achieve homeownership.
How has the decline of large-scale housing projects affected housing prices?
The decrease in large-scale housing projects has diminished the potential for cost-effective, mass-produced homes. As fewer large developments are built, competition decreases, leading to inflated housing prices, which aggravates the existing housing affordability crisis.
What are some potential solutions to the housing affordability crisis?
To address the housing affordability crisis, policymakers could consider reforming land-use regulations to encourage larger scale developments, reducing NIMBY policies that obstruct new housing projects, and supporting innovative construction practices that enhance productivity and lower costs.
How do housing market trends influence overall economic growth?
Housing market trends directly influence overall economic growth as housing affordability affects consumer spending, construction jobs, and overall financial stability. A healthy housing market promotes economic growth, whereas a stagnant or costly housing market can hinder economic progress, particularly for younger generations.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The increase in housing costs has made homeownership unattainable for many Americans. |
| NIMBY Land-Use Policies | ‘Not in my backyard’ policies have led to tighter land-use controls, adversely affecting productivity in the housing sector. |
| Decline in Construction Productivity | Between 1970 and 2000, construction productivity fell by 40%, while other sectors continued to grow. |
| Innovation Stagnation | Patenting in the construction sector declined post-1970, indicating a lack of innovation in housing construction. |
| Impact of Large Projects | Historically, large-scale housing projects boosted productivity, but today such projects are almost non-existent. |
| Wealth Disparity | Younger demographics are seeing a decrease in housing wealth, while older citizens are benefiting from appreciation. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a significant challenge that America is grappling with, driven largely by ineffective land-use regulations such as NIMBYism. These regulations have curtailed the potential for mass production in housing, leading to skyrocketing costs and diminishing opportunities for aspiring homeowners. As historical data illustrates, productivity in housing construction has dramatically declined since the 1970s, contrasting sharply with advances in other industries. Addressing this crisis requires a reevaluation of regulatory frameworks to foster innovation and increase the availability of affordable housing options.